I have started compiling the following, which others may benefit from and or contribute to: Statements regarding the transoral route versus the transcervical route to styloidectomy originating from peer-reviewed and recently published scientific papers; excluding preferably studies published to propose a particular method of either the transoral or transcervical archetype.
The surgical options consist of two approaches: the transoral and the transcervical routes. Advantages for the former include fewer postoperative cosmetic deformities and the relative ease of performance, though visualization may be poorer and the risk of causing damage to the adjacent neurovascular structures is increased (Sukegawa et al., 2017). Drawing from the findings here, this treatment approach is favored for classical cases, while hardly any vascular patients were treated in this manner; perhaps due to the pre-existing vulnerable state of the neurovascular structures. Instead, vascular patients are more likely to undergo a transcervical approach which may have a longer operative duration and postoperative cosmetic issues but in return provides an adequate field of operation with good surgical access to the styloid process and its surrounding tissues, hence avoiding unnecessary harm to adjacent structures (Sukegawa et al., 2017). The results showed a notably low occurrence of adverse events associated with the surgical intervention. These outcomes suggest a relatively favorable safety profile. However, transpharyngeal manipulation with a manual fracture of the elongated styloid process does not usually relieve symptoms and risks damage to adjacent neurovascular structures. The diversity of treatment options for Eagle syndrome reflects the absence of a standardized protocol. The lack of uniform guidelines may lead clinicians to rely on a broad range of methods and medical approaches based on individual observations and abilities.
In this study, the highest rate of complications was found in the intraoral approach.
(https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08869634.2021.2020995)
The selection of either transcervical or intraoral approach is a surgeon-dependent decision, which relies on surgeon’s experience, skills, and available equipment and may be influenced by the patient’s expectations. Despite the reported disadvantages of transcervical approach, various modifications of this technique have lessened the possible morbid consequences.
There were no significant differences between the effects of the intraoral and external cervical approaches
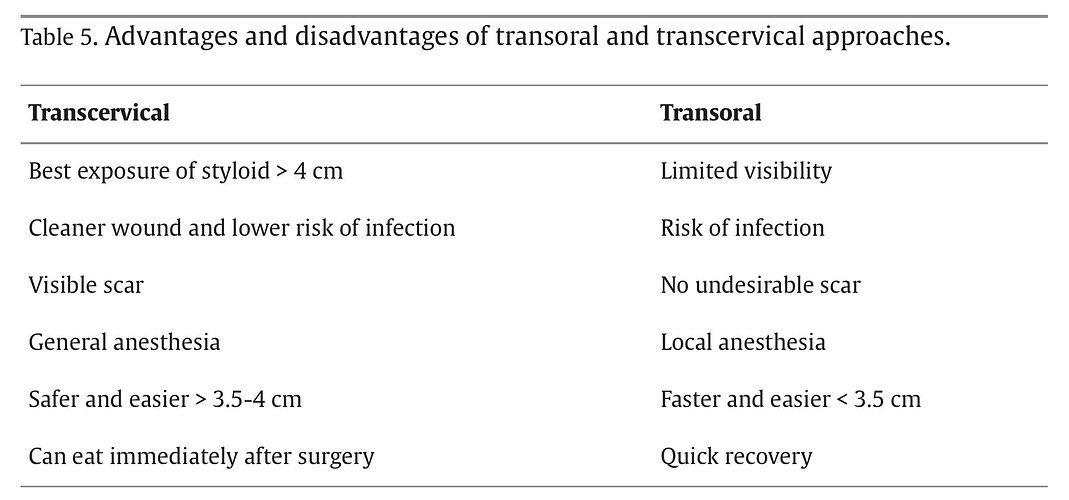
The message that could be obtained from this review is that neither approach has absolute advantages or disadvantages and that the choice of approach should be dependent on the surgeon’s preference as well as tailored to the patient. For convenience, the main advantages and disadvantages have been summarized in Table 5.
( Surgical approaches for bilateral Eagle’s syndrome: A narrative review of literature - ScienceDirect )
To conclude, a thorough preoperative evaluation is crucial to determining the appropriate approach for the removal of the styloid process. Factors such as the length of the process, the surgeon’s preference, the patient’s comorbidities, and mouth opening should be taken into consideration. If the styloid process is excessive and requires surgical removal, the extraoral approach offers a direct and anatomically significant method with good visualization and controlled management of major vessel hemorrhage. However, if the process can be easily identified trans-pharyngeal by palpation, then the intraoral approach is a preferred procedure. Overall, the choice of approach should be tailored to each patient based on their specific circumstances and the surgeon’s expertise
Personally, I like the table’s stance of “it depends” even though a blanket one-size-fits-all statement would be easier to work with.